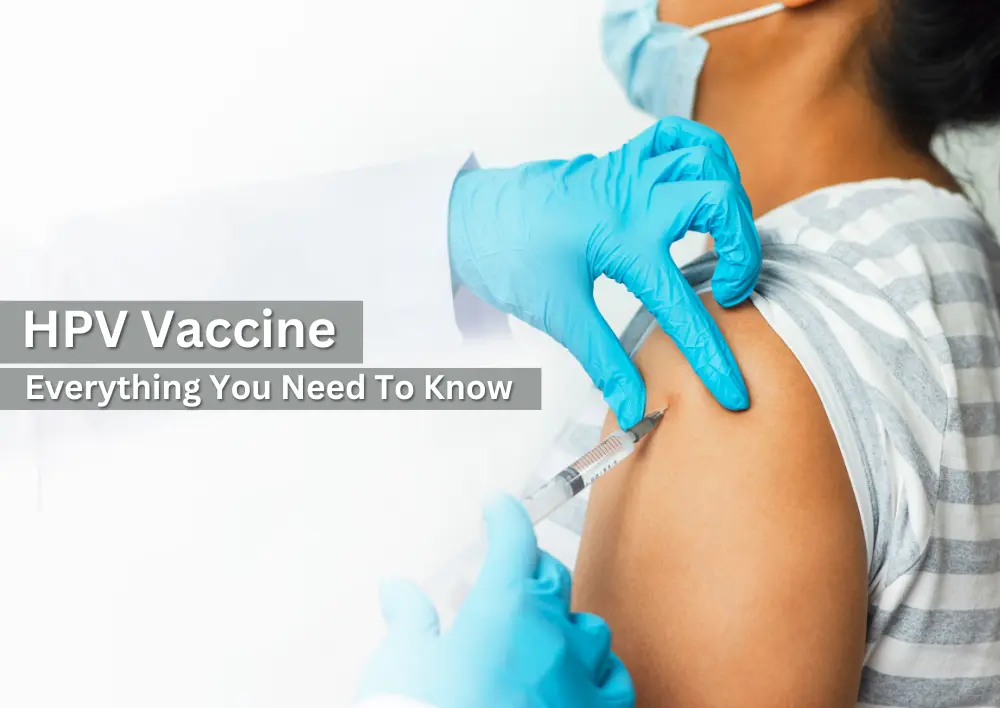
HPV Vaccine: Everything You Need To Know
Summary: The HPV vaccine plays an important role in preventing HPV-related cancers and genital warts. Administered through a series of doses, it is most effective when given to children and adolescents between 9-14 years, though it can still benefit adults up to 45. The vaccine provides long-lasting protection by helping the body’s immune system fight the virus before it causes harm. While generally safe, it's important to consult with a gynaecologist to determine the best vaccination schedule for you or your child.
Overview
Did you know that sexually transmitted infections (STIs) affect millions of people each year, and the HPV vaccine can help prevent many of them from turning into serious health problems?
HPV (Human Papillomavirus)is one of the most widespread sexually transmitted infections. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 80% of sexually active people are likely to contract it at some point in their lifetime.
While most infections are harmless and go away on their own, certain high-risk strains of HPV can lead to cervical cancer, genital warts, and cancers of the throat, anus, penis, vagina and vulva. Every year, millions of new cases of HPV-related cancers are reported globally, but many of them can be prevented with timely vaccination and routine screening with a PAP smear.
The HPV vaccine offers a safe and reliable way to shield yourself and your loved ones from serious health complications. In this blog, the best gynaecologist doctor in Gurgaon at Miracles Apollo Cradle shares expert insights on what the HPV vaccine is, who should get it, when it is recommended, and how it can help reduce your risk of HPV-related diseases.
What Is the HPV Vaccine?
The HPV vaccine is designed to protect against certain types of HPV that are most likely to cause cancer or genital warts. It helps your immune system recognize and fight the virus before it can cause harm. There are several types of HPV, but studies suggest that HPV types 16 and 18 are responsible for about 70% of cervical cancer cases. The vaccine also covers other strains linked to genital warts and other cancers. In India, Gardasil and Cervavac are the most commonly available vaccines. According to studies by NIH, CERVAVAC is an Indian-made new low-cost single-dose HPV vaccine that is not only effective but a game changer for India.
Why is the HPV Vaccine Important?
Let’s keep it simple; this vaccine helps your body build protection against the most harmful types of HPV. The types that cause up to 90% of cervical cancers and other serious health issues. Here is why getting the HPV vaccine is important:
1. Prevents Cancer
HPV is linked to several types of cancer:
-
Cervical cancer (almost all cases are caused by HPV)
-
Anal, vaginal, vulvar, penile, and throat cancers.
-
The vaccine protects against the high-risk strains of HPV that cause these cancers.
2. Protects Both Males and Females
-
Girls and women are protected from cervical, vaginal, and vulvar cancers.
-
Boys and men are protected from penile, anal, and throat cancers.
-
It also reduces the spread of the virus, protecting future partners.
3. Prevents Genital Warts
The vaccine also protects against the HPV types that cause genital warts, a common and distressing condition.
4. More Effective When Given Early
-
The vaccine works best when given before exposure to HPV, ideally between the ages of 9 to 14 years.
-
But it can still offer protection if given up to age 26, and in some cases, even up to 45.
5. Safe and Long-Lasting Protection
The HPV vaccine has been extensively studied and is proven safe and effective.
Just a two or three-dose series provides long-term protection.
When is the HPV vaccine given?
The HPV (Human Papillomavirus) vaccine is typically given in two or three doses, depending on the age of the person receiving the vaccine. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends the HPV vaccine for kids (both girls and boys) aged 9 to 14 and provides a vaccination schedule to ensure maximum protection against HPV-related diseases, including cancer. Here is the WHO's recommended HPV vaccine schedule:
1WHO HPV Vaccine Schedule:
For Children and Adolescents (Ages 9–14):
2-Dose Schedule:
The HPV vaccine is administered in two doses for individuals aged 9 to 14. The first dose can be given at any time within this age range, while the second dose is usually scheduled 6 to 12 months after the initial one.
The immune system of younger individuals responds well to the vaccine, providing strong protection after two doses.
For Adolescents and Young Adults (Ages 15–26):
3-Dose Schedule: If the HPV vaccine is started after the age of 15, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends a 3-dose schedule. The second dose should be given 1–2 months after the first, and the third dose should be given 6 months after the first dose. This schedule is important because individuals over 15 need more doses to develop a strong and long-lasting immune response.
For Adults (Ages 27–45):
Adults in this age range may still benefit from the vaccine, but the decision is usually based on individual health needs. It is recommended to consult a gynaecologist to see if the vaccine is appropriate.
How Does the HPV Vaccine Work?
The HPV vaccine activates the immune system to build protection against the strains of the virus. As it doesn’t contain a live virus, it cannot cause an HPV infection. Once vaccinated, the body produces antibodies that can recognize and combat the virus if encountered in the future.
Who Should Get the HPV Vaccine?
The HPV vaccine is most effective before exposure to the virus, which is why it is recommended at an early age.
Recommended age groups:
-
Children (boys and girls) of 9 to 14 years: This age group needs two doses.
-
Adolescents (15 years and above): Three doses recommended
-
Young adults: Women up to 26 years and men up to 21 years can also benefit
-
Adults aged 27 to 45: May consider vaccination after consulting a doctor
Even if someone is already sexually active, the vaccine can still offer partial protection from HPV types they have not been exposed to.
HPV vaccine's long-term side effects in females
The HPV vaccine is approved by the WHO, the CDC, and India’s Ministry of Health. It is generally well-tolerated and safe. Most side effects are mild and temporary.
-
Pain, redness, or swelling at the injection site
-
Mild fever
-
Headache
-
Tiredness
-
Nausea
-
Muscle/joint pain
-
Fainting or dizziness (usually in teenagers)
-
Mild allergic reactions, like rash (rare)
-
Serious side effects are extremely rare. Seek medical help if you experience:
-
Difficulty breathing
-
Swelling of the face or throat
-
Severe rash or hives
Conclusion:
HPV might be common, but it's serious consequences can be prevented. The HPV vaccine is one of the most effective ways to fight cervical and other HPV-related cancers. Whether you are a parent, a young adult, or someone who missed the vaccine earlier in life, it is never too late to learn and act. Consult a gynecologist doctor near you at Miracles Healthcare, understand your options, and take a proactive step toward a healthier future. Want to know if the HPV vaccine is right for you or your child? Book an appointment with our obstetrics and gynaecology experts and take a step towards cancer prevention.
Frequently Asked Questions
The HPV vaccine is given in 2 doses if started between the ages of 9–14. years, if started at 15 years or older, 3 doses are recommended for better immunity.
You can get the HPV vaccine from Miracles Apollo Cradle Gurgaon. We offer safe and reliable vaccination services under expert medical supervision. Book your appointment today for timely protection.
Yes, it is also recommended for boys as it helps prevent genital warts and certain cancers in males, too.
The ideal age for vaccination is between 9–14 years before sexual exposure. Catch-up vaccination can be given up to age 26 years.
Yes, it is over 90% effective in preventing HPV-related diseases if given early. It offers long-term protection against cervical and other cancers.
Gardasil-9 is the most effective HPV vaccine, offering protection against 9 HPV types. It covers more strains than earlier vaccines, such as Gardasil and Cervarix.
No, the HPV vaccine is for both males and females. It helps lower virus transmission and protects against HPV-related diseases.
You may experience mild pain, redness, or swelling at the injection site, but these side effects are usually temporary and resolve on their own.


_in_Pregnancy.webp)







Was the information useful?
0 0