Arthritis: Types, Causes, and Proven Treatments for Lasting Relief
Summary
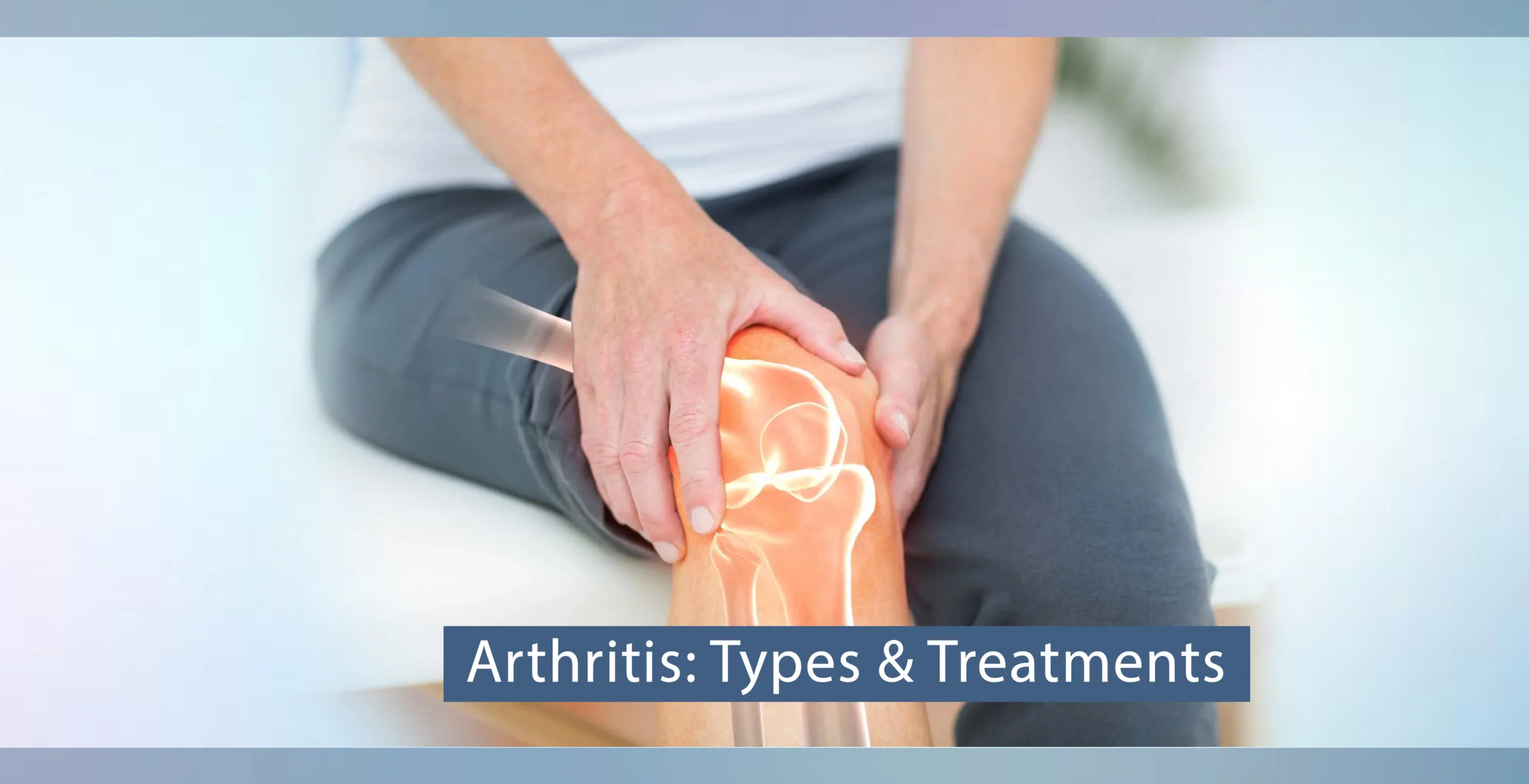
According to the studies, arthritis affects approximately 15% of the population in India, which translates to over 210 million people. This condition develops due to inflammation in the areas where two or more bones meet, such as the knee, shoulder, or even the smaller joints in your spine. The inflammation can lead to arthritis symptoms like pain, stiffness, and swelling, which limits your range of motion and significantly impacts your quality of life. In this blog post, the leading orthopedist at Miracles Apollo Cradle/Spectra in Gurgaon shares their expertise on the most common types of arthritis, including osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. We will also explore effective treatment options and practical strategies to manage arthritis, helping you live a fulfilling and active life.
Arthritis Definition
Arthritis is an umbrella term that encompasses over 100 different conditions affecting the joints. It can be caused by inflammation, infection, or degenerative modifications. While some forms of arthritis are temporary, others are severe conditions that may worsen over time.
Joint inflammation is a sign of arthritis, which can lead to pain, swelling, stiffness, and difficulty moving. As the inflammation persists, joint damage can occur, making early diagnosis and treatment necessary for managing symptoms and preventing further complications.
Types of Arthritis
1. Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis, commonly known as "wear and tear arthritis," is the most prevalent form of arthritis, especially affecting those over the age of 50. It typically develops due to aging or repetitive use of the joints over time.
Osteoarthritis Causes
Osteoarthritis develops slowly over time, when the cartilage covering the bones starts to degrade, causing the bones to rub against each other. As the cartilage thins out, bone spurs can develop, further increasing pain and discomfort.
Osteoarthritis Signs and Symptoms
The primary symptoms of osteoarthritis include:
-
Pain around the joint, particularly after prolonged use or inactivity
-
Joint stiffness is typically more intense in the morning.
-
Swelling due to inflammation
-
Limited mobility in the affected joint
Over time, osteoarthritis can interfere with daily activities, such as walking, climbing stairs, or getting in and out of chairs. If left untreated, this type of arthritis can result in irreversible joint damage.
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a long-term autoimmune condition that impacts the joints. Unlike osteoarthritis, which is caused by automatic wear and tear, rheumatoid arthritis occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s tissues. This type of arthritis usually affects the small joints in the hands, wrists, and feet but can affect joints throughout the body.
What causes Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder where the body's immune system mistakenly targets and attacks its healthy tissues. This causes the synovium to swell, resulting in pain, stiffness, and eventual joint deformity. The immune system's attack can also affect ligaments, tendons, and muscles around the joint, making movement even more difficult.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis include:
-
Joint pain and swelling, usually in the same joints on both sides of the body.
-
Stiffness typically intensifies in the morning or following periods of rest.
-
Fatigue, loss of appetite, and fever due to the systemic nature of the disease.
-
Deformity of the joints over time, especially in the fingers, wrists, and knees.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a lifelong condition that may have periods of remission, where symptoms improve or disappear for a time, followed by outbreaks.
Arthritis Treatment Options
Various treatments can help alleviate symptoms, slow the disease's progression, and enhance overall quality of life. The treatment plan will differ based on the type of arthritis, the severity of symptoms, and the individual's overall health condition.
1. Lifestyle Changes to Manage Arthritis
Adopting specific lifestyle changes can significantly impact arthritis symptoms and assist in managing the condition.
-
Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity is important for strengthening the muscles around the joints, improving flexibility, and reducing stiffness. While high-impact activities such as running may put stress on weight-bearing joints, low-impact exercises like walking, cycling, and swimming can be easier on the joints while providing benefits.
-
Get Plenty of Rest: Arthritis can cause fatigue, so it’s important to get enough rest. A full night’s sleep and short naps during the day can help your body recover and improve your ability to cope with symptoms.
-
Weight Management: Carrying excess weight can put additional pressure on weight-bearing joints, such as the knees and hips. Losing even a small amount of weight can ease pressure on the joints, helping to reduce pain and stiffness.
-
Physiotherapy: A physiotherapist designs an exercise plan customized to your needs. Physiotherapy can improve the range of motion and help you maintain mobility in the affected joints. Braces, splints, or shoe inserts may also provide support and relieve pain.
-
Medications for Arthritis Pain and Inflammation: Various medications are available to alleviate arthritis symptoms, with the most suitable option depending on the type and severity of the condition.
2. Over-the-Counter Medications
a) Acetaminophen can help with mild pain.
b) NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs) effectively alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
3. Prescription Medications
a) Corticosteroid injections can be administered directly into the affected joint to reduce inflammation and offer temporary relief.
b) Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) are used to slow the progression of rheumatoid arthritis by suppressing the immune system.
c) Biologic agents target specific parts of the immune system involved in inflammation, offering relief for patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
4. Surgical Options for Severe Arthritis
In some cases, arthritis can cause joint damage and disability, requiring surgical intervention. These procedures are considered when non-surgical treatments no longer provide relief.
-
Osteotomy: An osteotomy involves cutting and realigning the bones to improve the function of the joint. This procedure is often used for knee arthritis to reduce pain and improve mobility.
-
Synovectomy: In rheumatoid arthritis, a synovectomy involves removing the inflamed synovium lining from the joint to reduce pain and swelling.
-
Joint Fusion: In cases where the joint is severely damaged, joint fusion may be performed. This procedure fuses the bones in a joint, eliminating motion but relieving pain.
-
Joint Replacement Surgery: For advanced arthritis, especially in weight-bearing joints like the hip or knee, joint replacement may be recommended. This procedure involves substituting the damaged joint with an artificial one, significantly improving functionality and relieving pain.
-
Alternative Therapies: Some individuals find relief from arthritis pain through alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, massage, or herbal supplements. Always consult your doctor before trying any new treatment, as it may interfere with your prescribed medications.
Conclusion:
Arthritis may seem discouraging, but with the right treatment plan, lifestyle changes, and support, you can manage your condition and improve your quality of life. Whether through medications, exercise, or surgery, there are several options available to reduce pain, improve function, and keep you active. If you or someone you know is suffering from arthritis, consult an orthopedic doctor near you today. By working together, you can find a treatment plan that works best for you and regain control over your life. For expert advice and personalized treatment plans, visit or contact us to book an appointment today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Arthritis mainly occurs because of joint inflammation caused by factors like aging, wear and tear of cartilage, autoimmune disorders, genetics, or previous joint injuries.
Type 4 arthritis refers to Psoriatic Arthritis, an inflammatory joint condition related to psoriasis that causes joint pain, stiffness, and swelling.
Arthritis commonly starts after age 40, but it can also affect young adults in their 20s or 30s, especially because of injury, genetics, or autoimmune issues.
Rheumatoid arthritis is considered the most serious type because it is an autoimmune disease that can cause permanent joint damage and deformity if untreated.
Early signs include joint stiffness in the morning, pain during movement, mild swelling, and reduced range of motion.
The fastest relief comes from a combination of anti-inflammatory medication, physiotherapy, and lifestyle changes like regular exercise and a healthy diet.
Vegetables like tomatoes, potatoes, eggplants, bell peppers, and okra may worsen arthritis symptoms in some people due to solanine content.
Arthritis is confirmed through physical examination, X-rays, blood tests, and imaging studies like MRI to assess joint inflammation and damage.
Miracles Apollo Cradle/Spectra is one of the best hospitals in Gurgaon for arthritis treatment, offering expert orthopaedic care, advanced diagnostics, and personalized treatment plans.







.webp)





Was the information useful?
0 0